Introduction
How does the education system in USA work
The education system in the How does the education system in USA work we decentralize USA with each state having its own set of regulations and guidelines. This decentralization allows for a diverse range of approaches to How does the education system in USA work education, but it also creates variations in quality and resources.
The education system in the United States is a multifaceted and diverse structure that plays a critical role in shaping the country’s future. With its decentralized approach, emphasis on local control, and an array of options, the How does the education system in USA work American education system offers students a unique journey through their academic careers. In this article, we will explore how the education system How does the education system in USA work in the USA works, from its foundational stages to higher education and beyond.
How does the education system in USA work
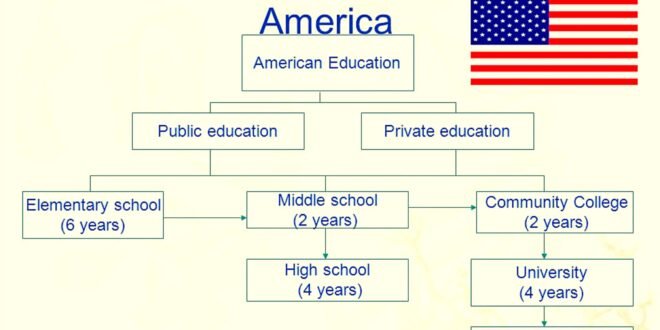
Pre-Primary Education
The journey through the American How does the education system in USA work begins with pre-primary education, which typically includes How does the education system in USA work preschool and kindergarten. This stage focusesHow does the education system in USA work on developing social skills, basic language abilities, How does the education system in USA work and early cognitive skills.
Primary Education
Primary education How does the education system in USA work encompasses elementary school spanning from first to fifth grade. Students receive a foundational How does the education system in USA work education in subjects like math, science, language arts, and social studies.
Secondary Education
Secondary education How does the education system in USA work comprises middle school and high school. Middle school, covering sixth to eighth grade, acts as a bridge between elementary and high school. We divide high school education into four grades and offers a wider range of subjects, often allowing students to choose electives based on their interests.
Post-Secondary Education
After high school, students can pursue post-secondary education, which includes colleges, universities, and vocational schools. Higher education provides specialized knowledge and skills in various fields, ranging from liberal arts to advanced sciences.
How does the education system in USA work
The Role of Local Control
One of the defining features of the American education system is the principle of local control. Educational decisions are largely made at the state and local levels, giving communities the authority to tailor their curriculum and policies to their specific needs.
Core Subjects and Curriculum
The curriculum in American schools typically includes core subjects like English, mathematics, science, and social studies. Additionally, schools often offer extracurricular activities such as sports, arts, and clubs, enhancing students’ overall development.
How does the education system in USA work
Standardized Testing
Standardized testing plays a significant role in the American education system. These tests aim to assess students’ academic progress and the effectiveness of schools and teachers. Common standardized tests include the SAT (Scholastic Assessment Test) and ACT (American College Testing).
How does the education system in USA work
Higher Education Options
The USA boasts a wide array of higher education options, including community colleges, four-year universities, and research institutions. These institutions offer diverse academic programs, catering to students’ individual career aspirations.
Vocational and Technical Training
Apart from traditional education, vocational and technical training programs provide hands-on skills for various careers. These programs are designed to equip students with practical expertise in fields such as mechanics, healthcare, and technology.
Challenges in the Education System
Despite its strengths, the American education system faces challenges. Disparities in funding between schools can lead to unequal opportunities for students. Additionally, concerns about standardized testing’s impact on teaching quality have sparked debates.
Advantages of the System
The flexibility of the education system allows students to explore diverse subjects and interests. The emphasis on extracurricular activities promotes holistic growth, and the decentralized structure encourages innovation in teaching methods.
Education Funding and Affordability
Education funding varies widely across states, leading to discrepancies in resources and opportunities. The cost of higher education is also a concern, prompting discussions about making college more affordable.
Homeschooling and Alternative Approaches
Homeschooling is a legal and increasingly popular option in the US. It allows parents to educate their children at home, tailoring the curriculum to their values and preferences.
Education and the Workforce
Education in the US is closely linked to the workforce. A well-educated workforce contributes to economic growth and innovation, making education a crucial factor in the nation’s success.
Technology Integration in Education
Technological advancements have revolutionized education, enabling personalized learning experiences and online education. Integrating technology prepares students for the digital age.
Inclusivity and Special Education
Inclusivity is a key principle, and schools provide special education services to students with disabilities. These programs aim to provide tailored support and equal learning opportunities.
Decentralization and Local Control
One of the defining features of the American education system is its decentralization. Unlike many countries with a centralized education authority, the US entrusts educational decision-making to individual states and local communities. This approach grants a significant degree of autonomy to local school districts, allowing them to tailor curriculum, teaching methods, and policies to their specific needs and priorities.
Each state operates its own department of education, responsible for setting guidelines, standards, and regulations for schools within its jurisdiction. This decentralization can lead to variations in education quality and resources across different states and districts.
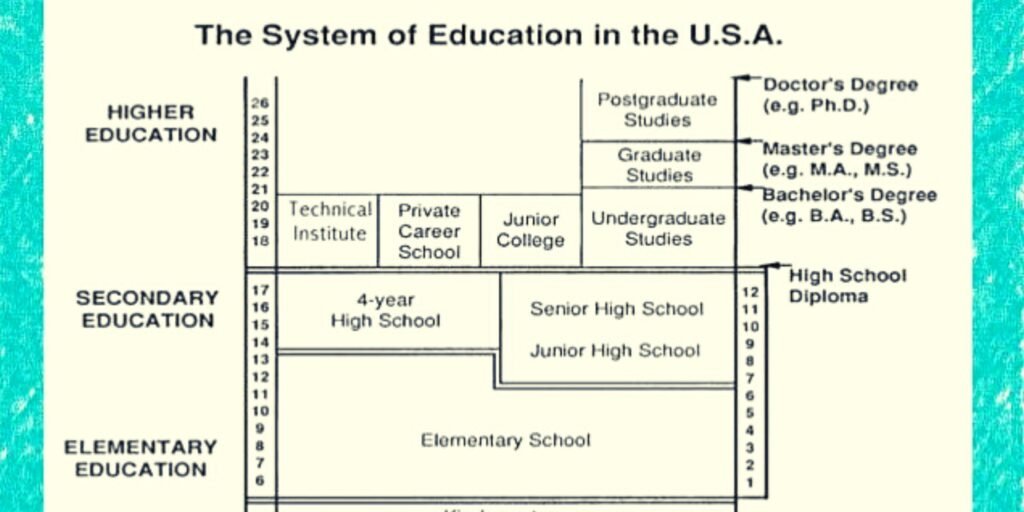
Early Childhood Education
The educational journey often begins with early childhood education, which includes preschool and kindergarten. While not compulsory, these years provide a foundation for young learners, focusing on social skills, basic numeracy, and language development.
Primary Education
Primary education, also known as elementary school, typically covers grades one through five or six, depending on the region. During these formative years, students are introduced to core subjects such as mathematics, English language arts, science, and social studies. Primary education aims to establish fundamental skills in reading, writing, and arithmetic.
Middle School and Junior High
Following primary education, students move on to middle school or junior high, spanning grades six through eight or seven through nine. This phase acts as a transition between elementary and high school, exposing students to a broader curriculum and helping them navigate the challenges of adolescence.
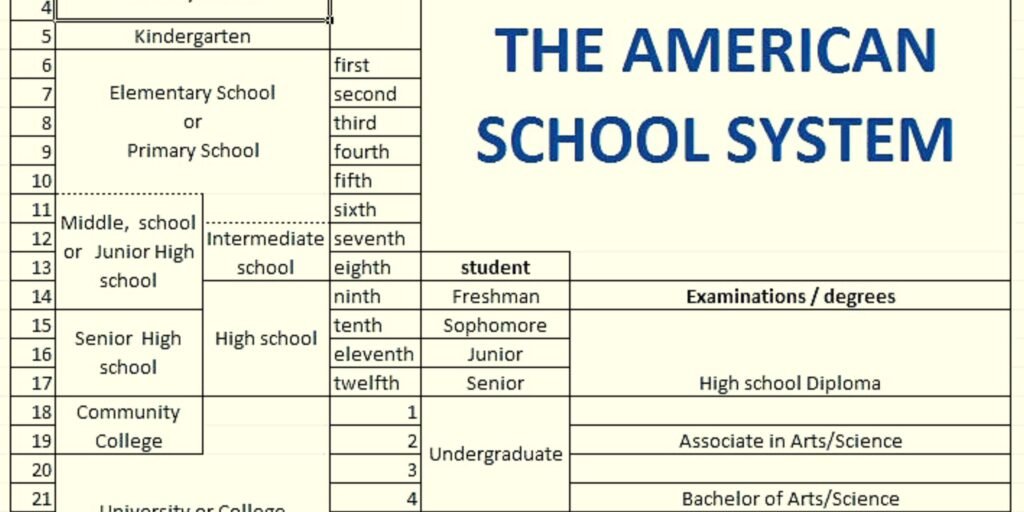
High School
High school education, typically covering grades nine through twelve, is a critical period for students as they prepare for higher education or the workforce. High schools offer a wide range of subjects, including advanced coursework, elective classes, and extracurricular activities. Students often have the flexibility to tailor their education to their interests and future goals.
Post-Secondary Education
Upon completing high school, students have the option to pursue post-secondary education. This includes community colleges, four-year universities, and vocational schools. Community colleges offer associate degrees and certificates, while universities provide bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees. Vocational schools focus on hands-on training for specific careers.
Core Curriculum and Electives
The American education system emphasizes a balanced curriculum that includes core subjects such as mathematics, science, English language arts, and social studies. This foundational knowledge equips students with essential skills for higher education and the workforce.
In addition to the core curriculum, students often have the opportunity to choose elective courses based on their interests. These electives can range from arts and music to computer science and foreign languages, allowing students to explore their passions and broaden their horizons.
Table of Contents
Introduction
Structure of the Education System
Pre-Primary Education
Primary Education
Secondary Education
Post-Secondary Education
The Role of Local Control
Core Subjects and Curriculum
Standardized Testing
Higher Education Options
Vocational and Technical Training
Challenges in the Education System
Advantages of the System
Education Funding and Affordability
Homeschooling and Alternative Approaches
Education and the Workforce
Technology Integration in Education
Inclusivity and Special Education
Conclusion
Standardized Testing and Assessments
Standardized testing is a significant aspect of the American education system. These tests are designed to measure students’ academic proficiency, evaluate schools’ performance, and guide educational policy decisions. Common standardized tests include the SAT (Scholastic Assessment Test) and the ACT (American College Testing), which are often required for college admissions.
Table of Contents
Higher Education Options
The USA offers a wide range of higher education options, catering to diverse interests and career aspirations. Students can choose from universities, liberal arts colleges, technical institutes, and community colleges. Universities are known for their research opportunities and offer bachelor’s, master’s, and doctoral degrees. Community colleges provide two-year associate degrees and serve as an affordable pathway to higher education.
How does the education system in USA work
Challenges and Opportunities
While the American education system offers numerous advantages, it also faces several challenges. Funding disparities between schools can lead to inequalities in resources and educational opportunities. Additionally, concerns about standardized testing’s impact on teaching quality and curriculum have sparked debates among educators and policymakers.
However, the system’s flexibility and emphasis on individualism also create opportunities for innovation. Charter schools, for instance, operate independently and experiment with unique teaching methods. Homeschooling is another alternative, allowing parents to take control of their child’s education.
How does the education system in USA work
How does the education system in USA work
Conclusion
The education system in the USA is characterized by its diversity, local control, and focus on holistic development. While challenges persist, the system’s strengths lie in its adaptability and commitment to nurturing well-rounded individuals.
The education system in the USA is a complex and multifaceted structure that reflects the country’s commitment to diversity and individualism. Decentralization, local control, and a wide variety of educational options define this system. From early childhood education to post-secondary studies, the USA offers a dynamic educational journey that prepares students for the challenges and opportunities of the future.
How does the education system in USA work
FAQs
Is education in the USA free?
Education in the US is not entirely free. While public schools offer free education up to high school, higher education often comes with costs.
Can international students attend American universities?
Yes, many American universities welcome international students, offering them diverse academic and cultural experiences.
How do charter schools differ from public schools?
Charter schools are publicly funded but operate independently, often with a specific educational approach or theme.
What is the significance of the SAT and ACT tests?
The SAT and ACT are standardized tests used for college admissions, assessing students’ readiness for higher education.
Are there alternatives to traditional college education?
Yes, vocational schools and community colleges provide alternative pathways to careers without pursuing traditional four-year degrees.
Is education in the USA free?
Education in the US is not entirely free. While public schools offer free education up to high school, higher education often comes with costs.
Can international students attend American universities?
Yes, many American universities welcome international students, offering them diverse academic and cultural experiences.
How do charter schools differ from public schools?
Charter schools are publicly funded but operate independently, often with a specific educational approach or theme.
What is the significance of the SAT and ACT tests?
The SAT and ACT are standardized tests used for college admissions, assessing students’ readiness for higher education.
Are there alternatives to traditional college education?
Yes, vocational schools and community colleges provide alternative pathways to careers without pursuing traditional four-year degrees.
 Insu Edu Tech Insurance, Education & Technology
Insu Edu Tech Insurance, Education & Technology