Introduction
In the complex world of healthcare in the United States, Are You Required To Have Health Insurance in USA one burning question lingers on the minds of many: “Are you required to have health insurance in the USA?” This article aims to shed light on this intricate topic by providing comprehensive insights into the various aspects of health insurance requirements in the United States Are You Required To Have Health Insurance in USA.
Understanding the Affordable Care Act
Are You Required To Have Health Insurance in USA
The Mandate: Individual Shared Responsibility Are You Required To Have Health Insurance in USA
The Affordable Care Act, often referred to as Obamacare, introduced the Individual Shared Responsibility provision. Under this mandate, most Americans are required to have a minimum level of health insurance coverage. Failure to do so could result in financial penalties when filing taxes.
Exemptions and Special Circumstances
Are You Required To Have Health Insurance in USA
Not everyone is obligated to obtain health insurance. Are You Required To Have Health Insurance in USA The ACA allows for certain exemptions and considerations for individuals facing unique circumstances, such as financial hardships or religious beliefs.
State-Specific Health Insurance Requirements
Varying Regulations
It’s important to note that health insurance requirements can vary from state to state. Some states have implemented their own healthcare laws and mandates, which may differ from the federal requirements under the ACA.
Medicaid Expansion
Are You Required To Have Health Insurance in USA
The ACA also introduced Medicaid expansion, which provides healthcare coverage to low-income individuals and families. Are You Required To Have Health Insurance in USA Eligibility for Medicaid can vary based on state-specific criteria.
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
Coverage Through Your Job
Many Americans receive health insurance coverage through their employers. In such cases, employers often share the cost of insurance premiums with their employees, making it a more affordable option.
The Role of the Employer Mandate
The ACA also includes the Employer Mandate, which requires certain large employers to offer health insurance coverage to their employees. This mandate ensures that a significant portion of the workforce has access to healthcare benefits through their jobs.
The Health Insurance Marketplace
Exploring Your Options
For those who don’t have access to employer-sponsored coverage, the Health Insurance Marketplace, established by the ACA, offers a platform to explore and purchase insurance plans. Subsidies are available to help make coverage more affordable for those who qualify.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
The Cost of Going Uninsured
While the penalty for not having health insurance was reduced to zero dollars starting in 2019, some states have introduced their own penalties for non-compliance. It’s crucial to be aware of these state-specific consequences.
The Importance of Health Insurance
Financial Security
Health insurance provides a safety net in the event of unexpected medical expenses. It helps individuals and families avoid crippling debt due to healthcare bills.
Access to Preventive Care
Having insurance encourages regular check-ups and preventive care, which can lead to early detection and better management of health conditions.
Peace of Mind
Knowing that you are covered in case of illness or injury provides peace of mind and reduces stress during challenging times.
Exploring Health Insurance Plans
Types of Health Insurance
When considering health insurance, it’s essential to understand the different types available:
Health Maintenance Organization (HMO): HMO plans require you to choose a primary care physician and generally offer lower out-of-pocket costs but limited flexibility in choosing healthcare providers.
Preferred Provider Organization (PPO): PPO plans offer more freedom to see specialists without referrals but may come with higher premiums and out-of-pocket expenses.
Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO): EPO plans combine features of both HMOs and PPOs, providing a network of preferred providers while allowing some out-of-network coverage in emergencies.
Point of Service (POS): POS plans necessitate a primary care physician and referrals for specialists but may offer more coverage for out-of-network services.
High Deductible Health Plan (HDHP): HDHPs have lower premiums but higher deductibles, often paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) for tax advantages.
Comparing Coverage and Costs
Each plan type has its benefits and drawbacks. It’s crucial to assess your healthcare needs, budget, and preferences when selecting a plan. Consider factors like monthly premiums, deductibles, copayments, and out-of-pocket maximums to determine which plan aligns best with your circumstances.
Navigating Open Enrollment
Timing Matters
Open enrollment periods are specific times when you can enroll in or make changes to your health insurance plan. For most individuals, open enrollment for health coverage through the Health Insurance Marketplace occurs annually, typically in the fall.
Special Enrollment Periods
Certain life events, such as getting married, having a baby, losing other coverage, or moving to a new state, may qualify you for a Special Enrollment Period outside the standard open enrollment window. It’s crucial to be aware of these opportunities to make changes to your coverage when necessary.
Utilizing Preventive Services
Stay Healthy, Save Money
Most health insurance plans cover preventive services at no cost to you. These services include vaccinations, screenings, and wellness check-ups. By taking advantage of these offerings, you can stay healthy and avoid potential health issues down the road.
Wellness Programs
Some health insurance plans offer wellness programs and incentives to encourage healthy living. These programs may include discounts on gym memberships, smoking cessation support, and weight management programs.
Understanding the Role of Health Insurance Agents
Expert Guidance
Navigating the complex world of health insurance can be daunting, especially when you consider the numerous plans, coverage options, and regulations. Health insurance agents or brokers can provide valuable assistance in this process.
Personalized Recommendations
Agents have an in-depth understanding of various insurance plans and can tailor their recommendations to your specific needs. They can help you find a plan that not only fits your budget but also covers the healthcare services you require.
No Additional Cost
It’s essential to note that using the services of a health insurance agent typically doesn’t cost you extra. They are compensated by the insurance companies, so you can benefit from their expertise at no additional expense.
The Importance of Routine Check-Ups
Prevention is Key
One of the core principles of healthcare is prevention. Routine check-ups with your primary care physician can detect health issues early, often before symptoms appear. This early detection can be critical in effectively managing and treating illnesses.
Building a Relationship
Regular visits to your doctor also allow you to build a relationship with your healthcare provider. This rapport can lead to more personalized care and a deeper understanding of your health needs.
Navigating Health Insurance Terminology
Don’t Get Lost in the Jargon
Health insurance comes with its own set of terms and acronyms that can be confusing. Understanding the basics can help you make more informed decisions about your coverage.
Premium: The amount you pay for your health insurance every month.
Deductible: The amount you must pay for covered healthcare services before your insurance plan starts to pay.
Copayment (Copay): A fixed amount you pay for a covered healthcare service, typically due at the time of service.
Coinsurance: Your share of the costs of a covered healthcare service, calculated as a percentage (e.g., 20%) of the allowed amount for the service.
Out-of-Pocket Maximum/Limit: The most you have to pay for covered services in a plan year. After you reach this amount, your plan pays 100% of the allowed amount for covered services.
Network: The facilities, providers, and suppliers your health insurer has contracted with to provide healthcare services.
In-Network: Services provided by healthcare providers or facilities that are part of your health plan’s network.
Out-of-Network: Services provided by healthcare providers or facilities that are not part of your health plan’s network.
Exploring Supplemental Health Coverage
Beyond Basic Coverage
While standard health insurance plans provide essential coverage, some individuals may opt for supplemental health insurance. These policies are designed to fill gaps in your primary coverage and offer added financial protection.
Dental and Vision Insurance
Many health insurance plans don’t include dental and vision coverage. Supplemental insurance for dental and vision can help cover expenses such as routine check-ups, glasses, or dental procedures.

Critical Illness and Accident Insurance
These policies provide a lump-sum payment if you’re diagnosed with a covered critical illness or experience an accident. This extra financial support can help cover medical bills, household expenses, or other costs during recovery.
Long-Term Care Insurance
Long-term care insurance covers the costs of services like nursing home care, assisted living, or in-home care. It’s particularly important for individuals concerned about future healthcare needs as they age.
Making Informed Choices
Weighing the Costs and Benefits
When considering supplemental health coverage, carefully assess your needs and budget. While these policies can provide valuable support, they also come with additional costs. It’s crucial to strike a balance that aligns with your financial situation.
Understanding Policy Details
Before purchasing any supplemental insurance, read the policy documents thoroughly. Understand what is covered, what isn’t, and any limitations or waiting periods that may apply. Being well-informed ensures that you get the most out of your coverage.
The Future of Health Insurance
Evolving Landscape
The world of health insurance is continually evolving. Changes in healthcare laws, advancements in medical technology, and shifting demographics all impact how insurance is provided and accessed.
Telehealth and Digital Solutions
The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of telehealth services, allowing patients to consult with healthcare providers remotely. The convenience and accessibility of telehealth are likely to play a significant role in the future of healthcare.
The Role of Education in Health Insurance
Empowering Consumers
Education is a powerful tool when it comes to health insurance. Empowering consumers with knowledge about their options, rights, and responsibilities can lead to better decision-making and improved health outcomes.
Resources for Learning
Numerous resources are available to help individuals understand health insurance better. Government websites, nonprofit organizations, and insurance companies themselves offer educational materials, guides, and webinars.
Working with Healthcare Navigators
Healthcare navigators are trained professionals who can assist individuals in understanding and enrolling in health insurance plans. They provide personalized guidance, helping you find the right coverage for your needs.
Advocating for Your Health
Understanding Your Coverage
To make the most of your health insurance, it’s vital to understand what your plan covers. Familiarize yourself with the network of healthcare providers, copayments, and any preauthorization requirements for specific procedures.
Appealing Coverage Denials
If your insurance provider denies coverage for a medically necessary procedure or treatment, you have the right to appeal the decision. Understanding this process and advocating for your health can be crucial in obtaining the care you need.
The Global Perspective
Contrasting Healthcare Systems
While this article has focused on health insurance in the United States, it’s valuable to compare the U.S. system with those in other countries. Many nations have universal healthcare, which provides coverage for all citizens and residents.
Lessons from Abroad
Studying healthcare systems abroad can offer insights into alternative approaches to providing healthcare. These insights can inform discussions about potential improvements in the U.S. system.
Your Health, Your Future
Taking Control
In the end, the question of whether you are required to have health insurance in the USA is just one part of a much larger conversation about your health and well-being. It’s a conversation that you have the power to shape.
The Power of Prevention
Prioritizing Your Health
One of the most significant advantages of having health insurance is the access it provides to preventive care. Regular check-ups, screenings, and vaccinations can detect health issues in their early stages, often before they become more serious and expensive to treat.
Saving Lives and Money
Preventive care isn’t just about staying healthy; it’s also about saving money. Catching and treating health conditions early can prevent costly medical procedures and hospital stays down the line.
The Human Element in Healthcare
Building Relationships
Healthcare isn’t just about insurance plans and policies; it’s about the people who provide care. Developing strong relationships with healthcare providers can lead to better communication, more personalized care, and improved health outcomes.
Mental Health Matters
Don’t forget that health insurance often includes coverage for mental health services. Access to therapists, counselors, and psychiatrists can be essential for maintaining your emotional well-being.
Preparing for Life’s Uncertainties
The Importance of Emergency Care
Health insurance ensures that you have access to emergency medical care when unexpected accidents or illnesses occur. It’s a safety net that can mean the difference between life and death in critical situations.
Planning for Parenthood
If you’re planning to start a family, health insurance is essential. Prenatal care, childbirth, and pediatric services are all covered under many health insurance plans, providing crucial support during this life-changing period.
Understanding the Individual Mandate
The concept of mandatory health insurance in the United States can be traced back to the Affordable Care Act (ACA), commonly known as Obamacare. Under this legislation, there was an individual mandate that required most Americans to have health insurance or pay a penalty. However, the individual mandate was effectively nullified in 2019 with the passage of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act.
The Repeal of the Individual Mandate
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act, signed into law in December 2017, eliminated the tax penalty associated with not having health insurance. This means that, as of 2019, there is no federal requirement for individuals to have health insurance or face financial penalties at the end of the year when filing taxes.
State-Level Requirements
While the federal mandate no longer exists, it’s important to note that some states have implemented their own individual mandates. For example, California, Massachusetts, and New Jersey have state-level mandates that require residents to have health insurance coverage or face state-specific penalties.
Penalties for Non-Compliance
The penalties for not having health insurance in states with individual mandates can vary widely. They are typically calculated based on income and other factors. Residents in these states should be aware of their specific state’s requirements and penalties to ensure compliance.
Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance
One of the most common ways Americans obtain health insurance is through their employers. Many employers offer health insurance benefits to full-time employees, and in some cases, they may be required to provide this coverage under the ACA.
The Role of Employers
While there is no federal mandate for individuals to have health insurance, there are requirements for certain large employers. Under the ACA, employers with 50 or more full-time employees are generally required to offer affordable health insurance coverage to their employees. Failure to do so can result in penalties for the employer.
Medicaid and Medicare
In addition to employer-sponsored coverage, there are government-run healthcare programs in the United States that provide health insurance to specific groups of people. These programs include Medicaid and Medicare.
Medicaid
Medicaid is a joint federal and state program that provides health insurance to low-income individuals and families. Eligibility and coverage can vary by state, but it serves as an important safety net for those who cannot afford private health insurance.

Medicare
Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily for individuals aged 65 and older, as well as certain younger individuals with disabilities. It consists of different parts that cover hospital care, medical services, and prescription drugs.
Health Insurance Options
For those who don’t have access to employer-sponsored coverage or qualify for government programs like Medicaid or Medicare, there are still options available in the private insurance market. Individuals and families can purchase health insurance plans through the Health Insurance Marketplace established by the ACA.
Navigating the Health Insurance Marketplace
The Health Insurance Marketplace allows individuals to compare and purchase health insurance plans that meet their needs and budget. Subsidies may also be available to help lower-income individuals and families afford coverage.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Flexible Spending Accounts
In addition to traditional health insurance options, individuals and families can also take advantage of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) to help manage healthcare expenses.
Health Savings Accounts
HSAs are tax-advantaged savings accounts that individuals with high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) can open. These accounts allow you to contribute pre-tax dollars, which can then be used to pay for qualified medical expenses. One significant benefit of HSAs is that the money you contribute rolls over from year to year, unlike Flexible Spending Accounts.
Flexible Spending Accounts
FSAs are similar to HSAs in that they allow you to use pre-tax dollars to pay for medical expenses. However, FSAs are typically offered through your employer and have a “use-it-or-lose-it” rule, meaning that any funds you don’t spend by the end of the plan year are forfeited. FSAs are a valuable tool for covering anticipated medical costs, such as co-pays and prescription medications.
Special Enrollment Periods
While there may not be a federal mandate requiring health insurance, there are specific times during the year when individuals can enroll in or make changes to their health insurance plans. This is known as the Open Enrollment Period. Additionally, life events such as getting married, having a child, or losing other coverage can trigger a Special Enrollment Period, allowing you to sign up for or modify your health insurance outside of the regular Open Enrollment Period.
The Importance of Having Health Insurance
Although you may not be legally required to have health insurance in many parts of the United States, it’s crucial to recognize the benefits of being insured. Health insurance provides financial protection in case of unexpected medical expenses, and it ensures you have access to necessary healthcare services when you need them. Without insurance, a serious illness or injury can lead to substantial medical bills that could potentially jeopardize your financial stability.
Access to Healthcare Services
Health insurance not only safeguards your financial well-being but also grants you access to a wide range of healthcare services. With coverage, you can visit doctors, specialists, and hospitals for check-ups, treatments, and preventive care. Regular medical check-ups can help detect health issues early, increasing your chances of successful treatment.
Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Flexible Spending Accounts
In addition to traditional health insurance options, individuals and families can also take advantage of Health Savings Accounts (HSAs) and Flexible Spending Accounts (FSAs) to help manage healthcare expenses.
Health Savings Accounts
HSAs are tax-advantaged savings accounts that individuals with high-deductible health plans (HDHPs) can open. These accounts allow you to contribute pre-tax dollars, which can then be used to pay for qualified medical expenses. One significant benefit of HSAs is that the money you contribute rolls over from year to year, unlike Flexible Spending Accounts.
Flexible Spending Accounts
FSAs are similar to HSAs in that they allow you to use pre-tax dollars to pay for medical expenses. However, FSAs are typically offered through your employer and have a “use-it-or-lose-it” rule, meaning that any funds you don’t spend by the end of the plan year are forfeited. FSAs are a valuable tool for covering anticipated medical costs, such as co-pays and prescription medications.
Special Enrollment Periods
While there may not be a federal mandate requiring health insurance, there are specific times during the year when individuals can enroll in or make changes to their health insurance plans. This is known as the Open Enrollment Period. Additionally, life events such as getting married, having a child, or losing other coverage can trigger a Special Enrollment Period, allowing you to sign up for or modify your health insurance outside of the regular Open Enrollment Period.
The Importance of Having Health Insurance
Although you may not be legally required to have health insurance in many parts of the United States, it’s crucial to recognize the benefits of being insured. Health insurance provides financial protection in case of unexpected medical expenses, and it ensures you have access to necessary healthcare services when you need them. Without insurance, a serious illness or injury can lead to substantial medical bills that could potentially jeopardize your financial stability.
Access to Healthcare Services
Health insurance not only safeguards your financial well-being but also grants you access to a wide range of healthcare services. With coverage, you can visit doctors, specialists, and hospitals for check-ups, treatments, and preventive care. Regular medical check-ups can help detect health issues early, increasing your chances of successful treatment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while the federal penalty for not having health insurance in the USA has been reduced to zero, there are still essential considerations at both the federal and state levels. Health insurance can be a vital tool for financial security, access to healthcare, and peace of mind. It’s advisable to stay informed about your specific state’s regulations and explore your options through the Health Insurance Marketplace.
FAQ
- Is health insurance mandatory in all states?
No, health insurance requirements vary from state to state in the USA. Some states have additional mandates and penalties for non-compliance. - Can I get financial assistance to purchase health insurance?
Yes, the Health Insurance Marketplace provides subsidies to make insurance coverage more affordable for those who qualify based on income and other factors. - What happens if I don’t have health insurance?
While there is no federal penalty for lacking health insurance, some states impose their own penalties. Additionally, going without insurance can leave you financially vulnerable in the event of a medical emergency. - Are there exemptions from the health insurance mandate?
Yes, the Affordable Care Act allows for exemptions based on factors such as income, religious beliefs, and specific life circumstances. - How can I find out about health insurance options in my state?
You can explore health insurance options in your state through the Health Insurance Marketplace or by contacting your state’s department of insurance for guidance.
 Insu Edu Tech Insurance, Education & Technology
Insu Edu Tech Insurance, Education & Technology


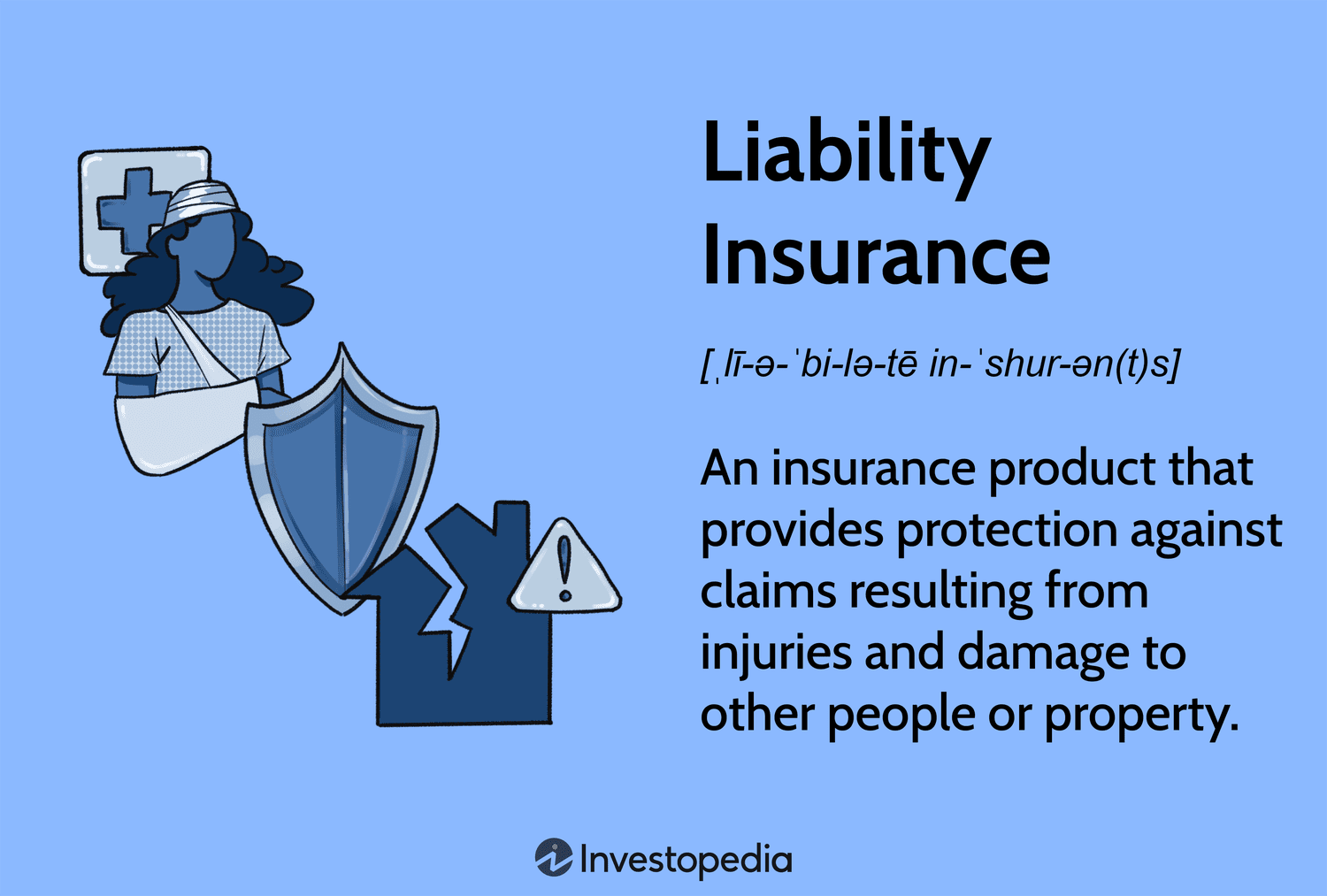

Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?